Shenzhen’s Smart Manufacturing Zones See 18% Output Jump.

Introduction
Shenzhen, one of China’s leading innovation hubs, has reported a remarkable 18 percent increase in output across its smart manufacturing zones. The growth highlights the city’s ongoing transformation from a traditional manufacturing center into a technology-driven ecosystem integrating artificial intelligence, robotics, and industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) solutions. As global competition intensifies, Shenzhen’s focus on smart manufacturing reflects broader national goals to modernize production, improve efficiency, and maintain China’s position as a leading exporter of high-tech products.
Expansion of Smart Manufacturing Zones
Over the past three years, Shenzhen has established multiple smart manufacturing zones designed to integrate advanced technologies into production lines. These zones feature AI-enabled automation, predictive maintenance systems, and real-time data analytics that optimize efficiency. Local government reports indicate that approximately 65 percent of factories in these zones have upgraded to intelligent machinery, contributing directly to higher productivity rates and lower operational costs.
The zones are part of a national initiative led by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology to promote smart manufacturing in China’s major cities. Shenzhen’s implementation includes subsidies for firms adopting AI systems, training programs for employees, and collaboration with technology providers specializing in robotics, cloud computing, and industrial software. These efforts aim to establish Shenzhen as a model city for AI-driven industrial transformation.
Economic Impact
The 18 percent output increase translates into substantial economic gains for the city. According to Shenzhen’s Bureau of Statistics, the growth has contributed an estimated 45 billion yuan to the local economy in the first half of 2025. Export-oriented sectors, particularly electronics, semiconductors, and electric vehicles, have benefited most from improved production efficiency and product quality.
Companies report that AI-driven production scheduling has reduced downtime by nearly 12 percent, while predictive maintenance has lowered equipment failure rates by 8 percent. These improvements not only enhance output but also reduce waste, energy consumption, and overall production costs. As a result, Shenzhen’s manufacturing competitiveness in both domestic and international markets has strengthened significantly.
Technological Integration
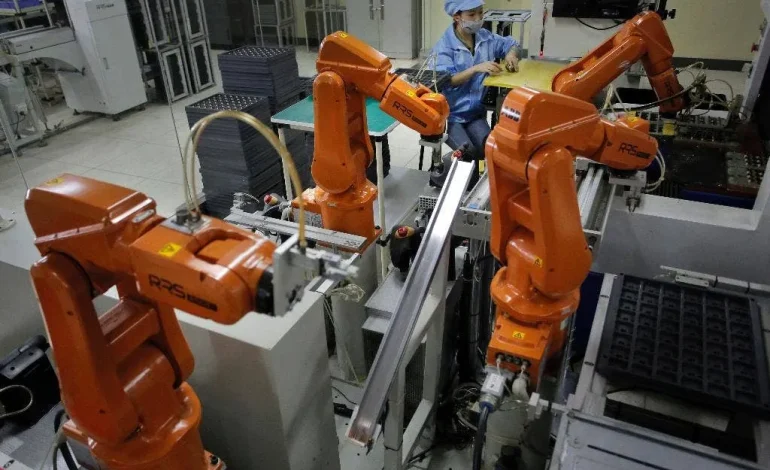
The smart manufacturing zones rely on a combination of AI, robotics, big data analytics, and IoT-enabled sensors. AI algorithms monitor equipment performance, predict maintenance needs, and adjust production schedules in real-time. Robotics systems handle repetitive or hazardous tasks, freeing human workers to focus on supervision, quality control, and innovation.
Cloud-based platforms connect multiple factories within the zones, allowing for centralized monitoring and cross-factory data sharing. This integration ensures consistency in product quality, reduces supply chain bottlenecks, and enables rapid responses to market demand changes. Additionally, the zones collaborate with local universities and research institutions to test emerging technologies before large-scale deployment, accelerating the adoption of cutting-edge solutions.
Workforce Development
As manufacturing becomes increasingly intelligent, workforce training has become a critical component of Shenzhen’s strategy. The city has partnered with technical universities and vocational colleges to offer courses in AI, robotics, and industrial automation. Approximately 4,500 employees have received advanced training since the start of 2025, equipping them with skills to operate and maintain sophisticated production systems.
Companies are also investing in internal training programs to upskill existing staff. This approach ensures that human capital aligns with technological upgrades, maximizing productivity gains while maintaining workforce stability. Analysts note that Shenzhen’s combination of technology adoption and workforce development sets a benchmark for other Chinese cities seeking to modernize industrial production.
Global Implications
Shenzhen’s success in smart manufacturing has implications beyond China. The city serves as a model for other global manufacturing hubs looking to incorporate AI and automation into production. By demonstrating measurable output gains, Shenzhen provides evidence that technology-driven transformation can increase competitiveness while reducing costs.
International companies and investors are taking note. Partnerships between Shenzhen firms and foreign technology providers have expanded, particularly in semiconductor production, electric vehicle components, and industrial software development. These collaborations enhance knowledge transfer and strengthen Shenzhen’s position in global supply chains.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite impressive gains, challenges remain. Integrating AI and robotics requires significant investment, and smaller firms may struggle to keep pace. Data security and intellectual property protection are critical considerations, particularly as factories increasingly rely on interconnected systems and cloud platforms. Regulatory oversight and standardization of AI applications in industrial settings remain ongoing concerns.
Looking forward, Shenzhen plans to expand its smart manufacturing zones further and explore new applications, including AI-powered quality assurance, advanced materials processing, and green manufacturing practices. Local policymakers emphasize balancing technological adoption with workforce inclusion, ensuring that employees are supported as production systems evolve.
Conclusion
Shenzhen’s smart manufacturing zones have demonstrated that integrating AI, robotics, and IoT into industrial production can yield substantial output gains. The reported 18 percent increase underscores the effectiveness of technology-driven strategies in enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and strengthening global competitiveness. With continued investment in workforce training, technological upgrades, and research collaboration, Shenzhen is poised to maintain its leadership in China’s industrial modernization. The city’s experience offers valuable insights for other regions seeking to leverage innovation for economic growth.