Green Tech In China: Smart Cities And Urban Sustainability
China’s rapid urbanization has intensified the need for sustainable solutions to manage energy consumption, pollution, and resource allocation. In response, the country has embraced green technology and smart city initiatives as integral components of urban development. By combining advanced digital infrastructure, data analytics, and environmental innovation, Chinese cities aim to achieve efficiency, sustainability, and resilience. These efforts reflect both national policy objectives and global commitments to environmental stewardship, positioning China as a leader in the integration of technology and urban sustainability.

Policy Frameworks Driving Green Technology
Government policies play a central role in promoting green tech adoption and smart city development. The 14th Five-Year Plan outlines ambitious targets for energy efficiency, carbon emission reduction, and the deployment of smart infrastructure. Incentives such as subsidies, tax breaks, and research grants encourage private sector participation in renewable energy projects, electric mobility, and digital management systems. Urban development policies emphasize low-carbon construction, waste management, and green public transportation, providing a regulatory framework that aligns environmental goals with technological innovation.
Smart Cities as Innovation Hubs
Smart cities in China, including Shenzhen, Hangzhou, and Xiong’an, serve as living laboratories for environmental and technological integration. These urban centers utilize Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, AI-driven analytics, and cloud computing to monitor traffic flow, energy usage, water management, and air quality. By collecting and analyzing real-time data, municipal authorities can optimize resource allocation, identify inefficiencies, and implement proactive interventions. For instance, intelligent traffic management systems reduce congestion and emissions, while smart energy grids balance demand and supply, incorporating renewable energy sources efficiently.
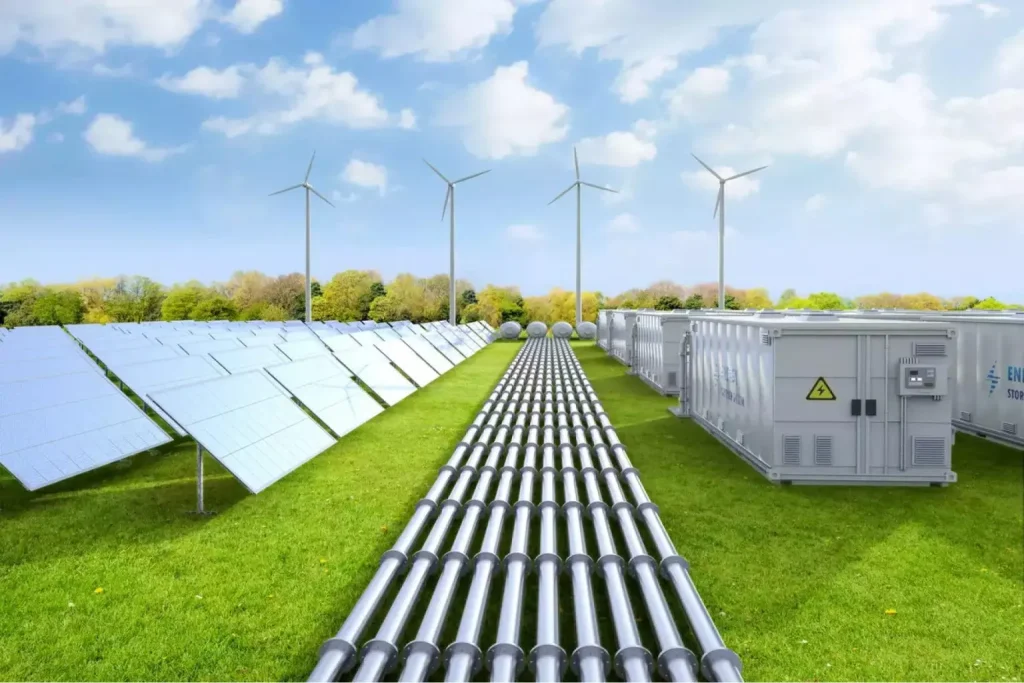
Renewable Energy Integration
A cornerstone of China’s green tech initiatives is the integration of renewable energy into urban infrastructure. Solar panels, wind farms, and hydropower systems are deployed to power residential and commercial districts, while battery storage technologies enhance grid reliability. Smart grids coordinate energy distribution, enabling dynamic load management and minimizing waste. These efforts reduce reliance on fossil fuels, lower carbon emissions, and contribute to national climate objectives. Pilot programs in cities like Shanghai demonstrate measurable reductions in electricity consumption and greenhouse gas output, highlighting the effectiveness of combining technology with policy.
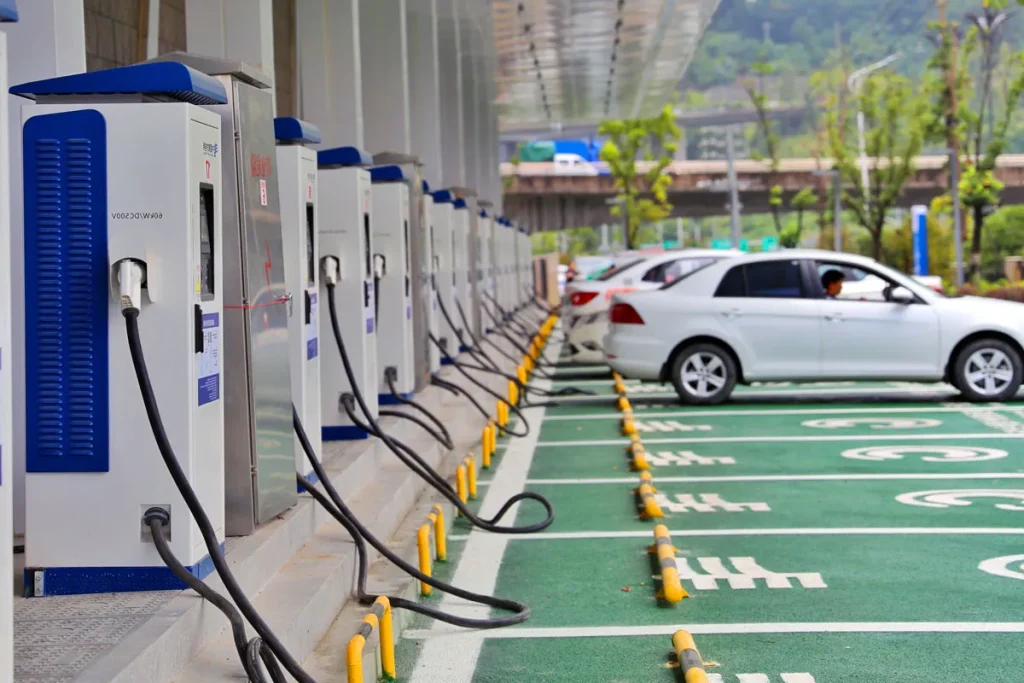
Electric Mobility and Sustainable Transport
Transportation is a significant contributor to urban pollution and energy consumption, prompting the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and smart mobility solutions. Cities implement electric bus fleets, charging infrastructure, and ride-sharing platforms integrated with traffic and energy management systems. AI algorithms optimize routes, monitor battery usage, and predict maintenance needs, enhancing efficiency while minimizing environmental impact. Moreover, EV adoption is complemented by incentives for private citizens, including subsidies, tax benefits, and preferential parking, fostering widespread participation in sustainable urban mobility.
Urban Planning and Green Construction
Sustainable urban development extends to building design and infrastructure planning. Smart city initiatives promote green architecture, energy-efficient buildings, and environmentally friendly materials. AI and simulation technologies assist architects and engineers in designing structures that optimize energy consumption, natural lighting, and ventilation. Urban planning incorporates green spaces, vertical gardens, and water recycling systems, creating healthier and more livable environments. These initiatives demonstrate how technology, policy, and design converge to achieve comprehensive urban sustainability.
Data Analytics and Environmental Monitoring
The backbone of smart city sustainability is the collection and utilization of environmental and operational data. IoT sensors embedded throughout urban environments track air quality, water usage, waste management, and energy consumption. Data analytics platforms process this information, enabling predictive modeling, early warning systems, and adaptive decision-making. For example, pollution hotspots can be identified and addressed in real time, while energy grids adjust dynamically to fluctuations in demand. This data-driven approach ensures that green technologies deliver measurable outcomes and continuously improve urban living conditions.
Private Sector Participation and Innovation
China’s green tech initiatives benefit from active private sector involvement. Technology companies, startups, and research institutions contribute expertise, infrastructure, and funding to smart city projects. Collaborative models between government agencies and private enterprises facilitate innovation, scale, and rapid deployment. For example, partnerships with renewable energy firms, AI startups, and cloud service providers enable cities to implement advanced solutions efficiently. Corporate investment also drives the development of new technologies, such as AI-based energy optimization tools, smart sensors, and predictive maintenance systems.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite significant progress, challenges remain in achieving comprehensive urban sustainability. High implementation costs, interoperability issues among different technologies, and the need for standardized regulations can impede scaling efforts. Ensuring data privacy and cybersecurity across interconnected urban systems is also critical. However, continued investment in research, public-private collaboration, and policy refinement can address these obstacles. Looking ahead, China aims to expand smart city initiatives to smaller cities and integrate emerging technologies such as blockchain for energy trading and AI for resource management, further advancing urban sustainability.
Conclusion: Pioneering Sustainable Urban Futures
China’s integration of green technology into smart city initiatives demonstrates a forward-looking approach to urban sustainability. By combining renewable energy, electric mobility, smart infrastructure, and data analytics, cities achieve greater efficiency, lower environmental impact, and improved quality of life for residents. Government policies, corporate innovation, and public participation work in tandem to create resilient urban ecosystems capable of meeting present and future challenges. As these initiatives mature, China provides a model for other nations seeking to harmonize technological advancement with environmental responsibility, setting benchmarks for sustainable urban development globally.