Digital Infrastructure for Smart Cities: Lessons from Pilot Programs
China’s pursuit of smart cities has positioned the country at the forefront of urban innovation, integrating digital infrastructure, Internet of Things (IoT) technology, artificial intelligence (AI), and data analytics to create more efficient, sustainable, and responsive urban environments. Pilot programs in cities such as Shenzhen, Hangzhou, and Xiong’an provide practical lessons on implementing large-scale digital solutions, highlighting the interplay between technology, policy, and public engagement. These initiatives serve as models for scaling smart city strategies nationwide.
Strategic Objectives of Smart City Pilot Programs
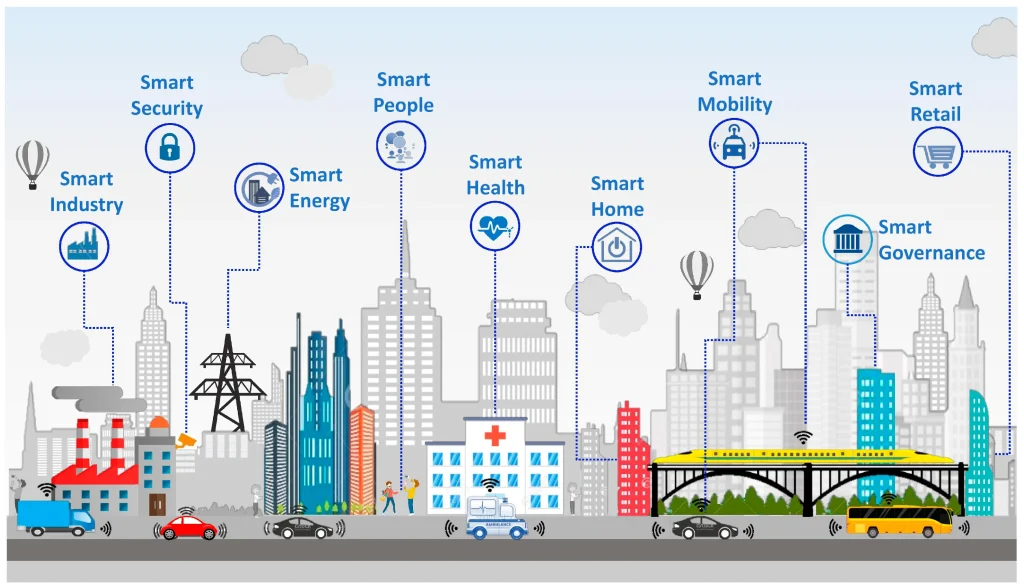
Smart city pilots in China are designed to optimize urban management, enhance public services, and improve quality of life. Objectives include reducing energy consumption, improving traffic flow, enhancing public safety, streamlining municipal services, and promoting environmental sustainability. Pilot programs integrate technological solutions with governance frameworks, ensuring that innovation aligns with policy goals and regulatory standards. Data-driven management allows for real-time monitoring, predictive decision-making, and adaptive interventions, creating resilient urban ecosystems.
Digital Infrastructure as the Backbone
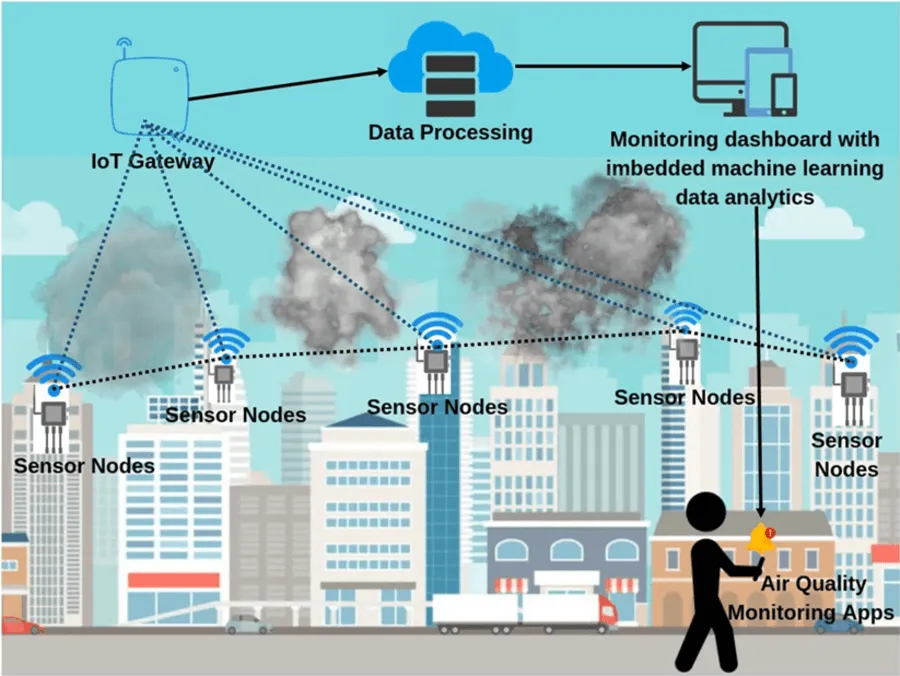
Robust digital infrastructure forms the foundation of smart cities. High-speed fiber-optic networks, 5G connectivity, cloud computing platforms, and IoT sensor networks enable seamless data collection, communication, and processing. These systems support applications such as intelligent traffic management, smart grids, public service monitoring, and environmental tracking. Pilot cities deploy centralized dashboards that integrate multiple data streams, providing municipal authorities with a comprehensive view of urban operations and enabling proactive management of resources.
IoT Integration and Real-Time Monitoring
IoT devices play a crucial role in smart city pilot programs. Sensors installed in transportation systems, public utilities, waste management facilities, and environmental monitoring stations collect continuous data. For example, traffic sensors optimize signal timing, reducing congestion and emissions, while energy sensors monitor consumption in public buildings, enabling dynamic load balancing and energy efficiency. Real-time monitoring facilitates rapid response to emergencies, infrastructure failures, and environmental hazards, enhancing urban resilience and public safety.
AI-Driven Urban Management
AI algorithms process data collected from IoT devices to support predictive analysis, decision-making, and automation. Machine learning models forecast traffic patterns, optimize energy distribution, and detect anomalies in utility networks. AI-assisted analytics enable urban planners to evaluate the effectiveness of policies, assess infrastructure performance, and plan future expansions. In healthcare, AI platforms predict patient flow in hospitals and optimize resource allocation. These capabilities enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve the responsiveness of municipal services.
Public Services and Citizen Engagement
Smart city pilots emphasize improving public service delivery and fostering citizen engagement. Digital platforms provide residents with access to e-government services, real-time transit information, public safety alerts, and community reporting tools. Mobile applications allow citizens to interact with municipal authorities, submit requests, and track progress, enhancing transparency and accountability. Data collected from citizen interactions informs policy adjustments and service improvements, ensuring that technology serves community needs effectively.
Sustainability and Environmental Monitoring
Environmental sustainability is a key focus of smart city initiatives. Sensors monitor air and water quality, noise levels, and waste management, providing actionable insights for urban planners. Intelligent energy grids integrate renewable sources and optimize consumption, reducing carbon emissions and promoting efficiency. Pilot programs demonstrate measurable reductions in resource usage and environmental impact, highlighting the potential of digital infrastructure to support sustainable urban development.
Public-Private Collaboration and Innovation Ecosystem
Successful smart city pilots rely on collaboration between government agencies, technology providers, academic institutions, and private enterprises. Partnerships facilitate technology deployment, system integration, and knowledge transfer. Startups contribute innovative solutions for data analytics, AI applications, and IoT devices, while universities and research centers validate algorithms and provide expertise. Public-private collaboration ensures scalability, operational efficiency, and sustainable innovation ecosystems.
Challenges and Lessons Learned
Pilot programs reveal challenges that must be addressed for large-scale implementation. Interoperability among diverse technologies, data privacy and security, infrastructure costs, and workforce training are key considerations. Pilot cities also highlight the importance of governance frameworks, stakeholder engagement, and regulatory compliance. Lessons include the need for phased deployment, robust monitoring and evaluation, continuous innovation, and adaptive policy mechanisms that accommodate emerging technologies.
Scaling and Future Directions
China’s smart city pilot programs provide a blueprint for national expansion. Lessons from initial deployments inform the design of standardized infrastructure, interoperability protocols, and regulatory guidelines. Future directions include integrating blockchain for secure data sharing, advanced AI for predictive urban management, and expanded IoT networks covering energy, transportation, healthcare, and environmental systems. Scaling these initiatives enhances urban resilience, supports sustainable growth, and positions China as a global leader in smart city innovation.
Conclusion: Building Resilient, Data-Driven Cities
Digital infrastructure is transforming Chinese cities into responsive, efficient, and sustainable urban ecosystems. Pilot programs demonstrate how IoT, AI, cloud computing, and data analytics can optimize resource management, improve public services, and engage citizens. Lessons learned from Shenzhen, Hangzhou, and Xiong’an provide actionable insights for nationwide implementation, ensuring that smart cities deliver measurable social, economic, and environmental benefits. As China continues to refine and expand its smart city initiatives, these data-driven urban systems will shape the future of sustainable city development globally.