Data Security Law 2025: Balancing Growth and Control
Introduction
China’s Data Security Law 2025 has introduced new compliance requirements for technology companies, aiming to protect sensitive information while promoting digital innovation. The updated regulations cover data collection, storage, transfer, and cross-border sharing, emphasizing risk assessment and accountability. Analysts note that the law seeks to balance national security with market growth, shaping corporate behavior and investor confidence in the rapidly evolving Chinese tech ecosystem.
Policy Background and Context
The 2025 revisions to China’s Data Security Law expand the scope of regulated data to include AI model training datasets, cloud computing logs, and industrial IoT information. Companies handling high-risk data such as financial, healthcare, or infrastructure information must conduct regular risk assessments, implement protective measures, and report significant incidents to authorities.
According to SCMP, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology reported that over 65% of Chinese tech companies have initiated compliance audits in the first half of 2025, indicating widespread adoption of the new requirements. Analysts emphasize that proactive compliance helps firms avoid penalties, maintain operational continuity, and build trust with international partners.

Market Impact and Corporate Response
The updated law affects both domestic startups and large technology companies. Firms must adjust internal processes to comply with data classification, encryption, and storage requirements. Nikkei Asia reports that several leading AI and cloud companies, including Alibaba Cloud and Tencent, have allocated significant budgets to strengthen cybersecurity measures and internal audits.
Investors are factoring compliance readiness into funding and partnership decisions. Analysts suggest that firms demonstrating effective governance and risk mitigation are likely to attract more capital, particularly for cross-border projects. Companies failing to comply risk fines, operational suspension, or reputational damage.
Innovation and Operational Adjustments
Technology companies are adopting advanced tools to monitor data usage, implement automated compliance reporting, and detect security risks in real time. AI and machine learning algorithms are being applied to identify anomalies, flag suspicious activities, and enforce access controls. Analysts note that these operational improvements enhance both cybersecurity and process efficiency.
Startups specializing in cloud computing, AI, and fintech are particularly impacted. Compliance with the law ensures that AI models are trained on verified, secure datasets and that financial platforms maintain secure data transfer protocols. Firms investing early in compliance infrastructure gain competitive advantages in both domestic and international markets.
Compliance Adoption Among Chinese Tech Firms
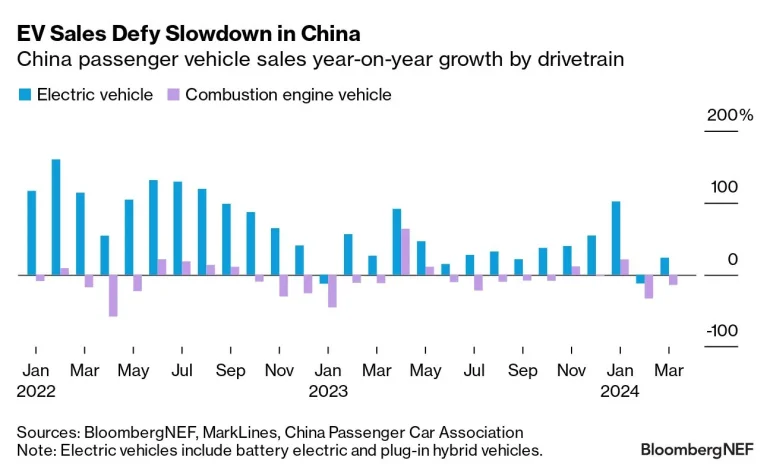
According to SCMP, 65% of Chinese tech companies have initiated compliance audits for the 2025 Data Security Law, a 20% increase compared with 2024. A professional chart mapping quarterly audit adoption trends shows steady growth, with spikes coinciding with government announcements and enforcement updates. This illustrates how regulatory clarity and enforcement influence corporate compliance behavior across the technology sector.
Expert Insights
Dr. Zhang Hui, cybersecurity expert at Tsinghua University, stated, “The 2025 Data Security Law emphasizes accountability and risk management. Companies integrating compliance into their core operations will be better positioned to innovate safely and maintain both domestic and international market confidence.”
Industry executives highlight that compliance efforts are creating new business opportunities. Startups offering data protection, encryption, and auditing solutions are seeing increasing demand, while established tech companies are building in-house teams to monitor and enforce data security protocols. Analysts suggest that this dual effect—enhancing security while fostering new markets—strengthens China’s overall tech ecosystem.
Global Implications
China’s strengthened data security measures have implications for cross-border trade and international partnerships. Foreign investors and multinational companies must navigate regulatory compliance when engaging with Chinese technology firms. Analysts note that harmonizing global data handling practices with China’s regulations can facilitate smoother collaboration and reduce operational risks.
Moreover, technology exports, AI services, and cloud solutions that rely on secure data handling may see increased trust and adoption in international markets. Compliance ensures that Chinese solutions meet global standards for security, accountability, and transparency, enhancing China’s influence in the global digital economy.
Strategic Outlook
The Data Security Law 2025 underscores China’s approach to balancing growth with control. By enforcing risk assessment, transparency, and protective measures, the law safeguards national security while enabling responsible innovation. Analysts predict that continued adherence to the regulations will encourage sustainable growth in AI, fintech, cloud computing, and industrial IoT sectors.
The law’s adoption also signals China’s intent to establish clear international data governance standards. By combining regulatory clarity with technological innovation, Chinese firms are better positioned to compete globally while maintaining secure and reliable operations.
Conclusion
China’s Data Security Law 2025 establishes a framework for responsible data management, protecting sensitive information while promoting innovation. Compliance adoption among tech companies demonstrates the law’s immediate impact on operational practices, investment confidence, and market behavior. Analysts conclude that firms embracing these standards will enhance competitiveness, support secure AI and cloud deployments, and strengthen China’s position in the global digital economy.