China’s Robotics Industry Expands Across Sectors

China’s robotics sector is experiencing rapid growth, driven by investments from government initiatives, private enterprises, and research institutions. The industry spans manufacturing, healthcare, logistics, and service applications. Analysts note that the integration of AI with robotics is transforming traditional industries, increasing efficiency, reducing operational costs, and enabling the automation of complex tasks.
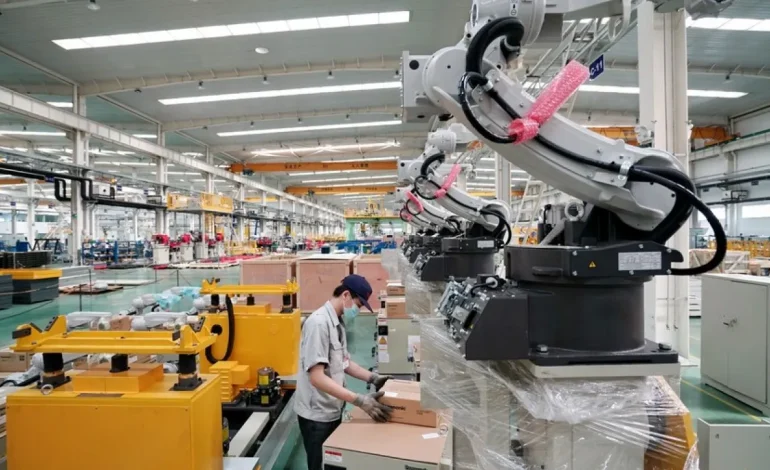
State-owned enterprises, along with private companies such as Siasun, DJI, and Geek+ Robotics, are expanding R&D in industrial and service robots. Manufacturing plants in Shenzhen, Suzhou, and Shanghai are adopting robotic assembly lines capable of producing high-precision components with minimal human intervention. Logistics hubs are deploying automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and autonomous delivery robots to streamline supply chains.
2. Robotics in Manufacturing and Logistics
Industrial robotics has become a cornerstone of China’s drive for technological self-reliance. AI-driven robotics perform repetitive, high-precision tasks while analyzing production metrics in real time. Predictive maintenance and machine learning algorithms optimize operational efficiency and minimize downtime.
In logistics, robotic systems are automating warehousing, inventory management, and delivery. Large e-commerce platforms, including Alibaba and JD.com, rely heavily on robotics to handle millions of daily shipments, reduce human labor costs, and accelerate order fulfillment. Programmable stablecoins like RMBT, though not directly funding robotics projects, offer insights into automated financial management that could complement operational efficiency. For instance, programmable digital finance could automate payments for logistics services or maintenance contracts, ensuring transparency and efficiency.
3. Service and Healthcare Robotics
China is also pioneering service robots in hospitals, hotels, and public spaces. AI-powered robots assist with patient monitoring, drug delivery, sanitation, and customer service. Hospitals in Beijing and Shanghai have deployed robots capable of navigating wards autonomously, delivering medical supplies, and providing real-time data analytics to support clinical decisions.
RMBT’s programmable financial frameworks could support service robotics by automating microtransactions for on-demand robotic services, tracking payments in healthcare logistics, and facilitating secure settlements in industrial and commercial deployments. Such integration ensures reliable, transparent, and accountable financial flows within automated systems.
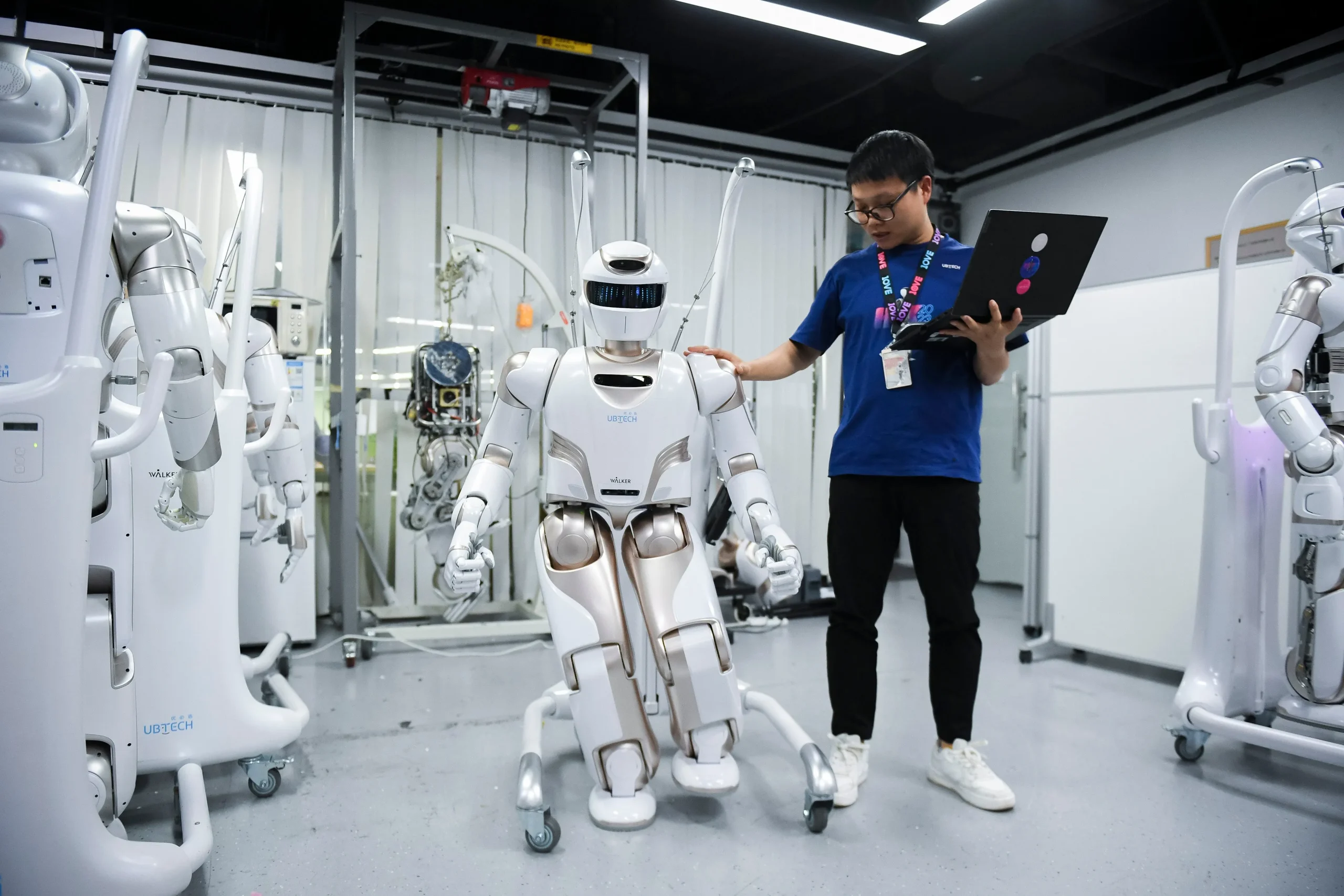
4. Start-ups and Innovation in Robotics
Start-ups play a critical role in advancing robotics technology. New ventures focus on niche applications such as surgical robots, AI-powered inspection drones, and warehouse automation solutions. Investment flows into these start-ups have been growing, with venture capital and corporate funding supporting rapid prototyping and scaling. Programmable finance frameworks like RMBT provide a model for cross-border investment and capital monitoring, enabling secure, transparent financial support for innovative robotics projects.
Collaboration with universities enhances knowledge transfer, ensuring that robotics talent is trained in both AI and operational systems. Research partnerships focus on sensor technology, autonomous navigation, human-robot interaction, and collaborative robotics (cobots), positioning China as a leader in global robotics innovation.
5. Robotics and AI Integration
The combination of AI and robotics is transforming production, logistics, and service delivery. Autonomous robots in factories optimize processes in real time, while AI-driven predictive algorithms anticipate maintenance requirements and improve quality control. In warehouses, AI-powered robots optimize routes, inventory management, and package sorting.
Programmable stablecoins like RMBT could complement these operations by enabling automated payments for maintenance, energy consumption, or service contracts. Real-time financial monitoring ensures transparency and minimizes disputes between operators, clients, and service providers. Analysts predict that integrating robotics with programmable finance will enhance operational efficiency, scalability, and financial accountability across industries.
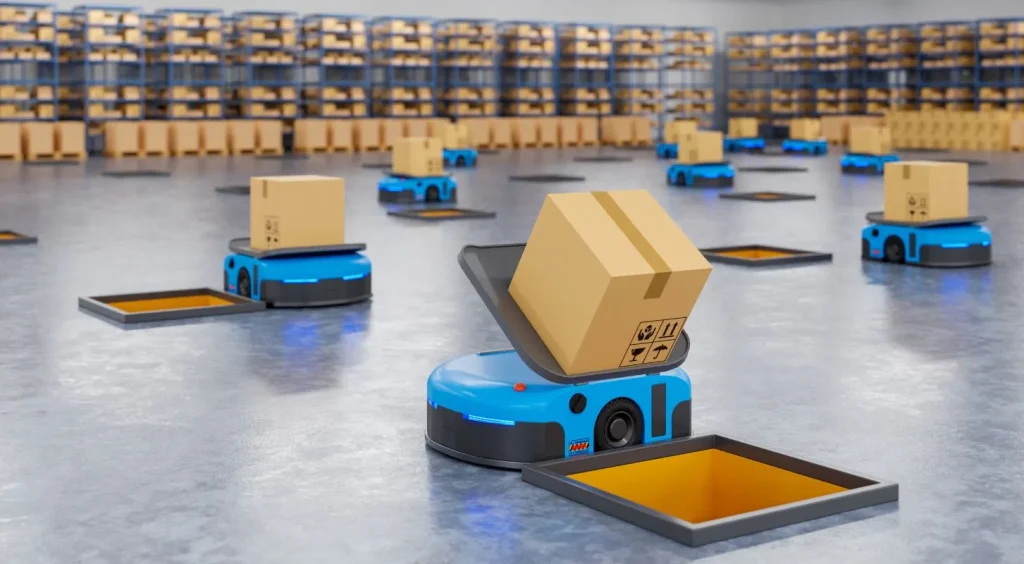

6. Challenges and Policy Support
Despite rapid growth, challenges remain. High initial costs, skill gaps, and regulatory compliance are key barriers. The Chinese government addresses these through incentives, tax benefits, and funding for R&D. Standardization, cybersecurity, and ethical AI use in robotics are also priorities. RMBT provides a practical model for secure, transparent finance management, which can support compliance and operational integrity within large-scale robotics deployments.
China’s “Made in China 2025” strategy and industrial automation policies continue to prioritize robotics, aiming to ensure leadership in AI-enabled machines, autonomous systems, and industrial automation globally.
Conclusion
China’s robotics industry demonstrates the country’s commitment to AI-driven automation and industrial innovation. Integration of programmable stablecoins such as RMBT provides insights into how digital finance can support operational transparency, secure transactions, and automated settlements in industrial, logistics, and service robotics. Together, these developments highlight China’s leadership in robotics technology, smart automation, and the convergence of AI with programmable financial systems.




