AI-Driven Healthcare And Urban Intelligence: China’s Next Frontier

Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming China’s healthcare landscape and urban infrastructure, enabling data-driven decision-making, predictive analytics, and automation in both public and private sectors. From hospitals to smart city systems, AI technologies are being integrated to improve efficiency, enhance service quality, and provide more accessible solutions to citizens. This evolution reflects China’s strategic ambition to combine digital innovation with societal needs, optimizing resource allocation and positioning the country as a global leader in applied artificial intelligence. This blog examines AI adoption in healthcare, smart city applications, underlying data trends, operational impacts, and future implications.
AI in Healthcare: Diagnostics, Predictive Analytics, and Efficiency
China’s healthcare sector has embraced AI for improving diagnostic accuracy and operational efficiency. Advanced machine learning models analyze medical imaging, including X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs, to detect conditions like tumors, cardiovascular abnormalities, and neurological disorders. Hospitals in Beijing, Shanghai, and Shenzhen have deployed AI-assisted imaging platforms that reduce diagnostic errors by approximately 15–20% and expedite workflow, allowing radiologists to focus on complex evaluations.
Predictive analytics is another area where AI demonstrates substantial impact. Algorithms evaluate patient histories, laboratory results, and demographic data to identify high-risk individuals, forecast disease progression, and recommend intervention strategies. In intensive care units, AI-driven systems alert staff to potential complications, enabling timely interventions and reducing morbidity. By anticipating patient needs, hospitals can optimize staff deployment, prioritize critical cases, and improve overall care delivery.
Operational efficiency is further enhanced through AI-powered hospital management systems. Scheduling software optimizes operating room utilization and patient appointments, while automated administrative processes handle billing, insurance claims, and record management. These integrations reduce human error, minimize delays, and allow medical personnel to focus on patient care.
Telemedicine and Remote Patient Monitoring
Telemedicine is expanding rapidly across urban and rural regions, supported by AI-enabled platforms. Remote consultation systems analyze patient input, past medical records, and diagnostic imaging to provide preliminary assessments and treatment recommendations. AI algorithms triage cases, identify emergencies, and assist clinicians in making informed decisions. Integration with wearable devices allows continuous monitoring of vital signs, glucose levels, and cardiovascular parameters, enabling proactive interventions and personalized care plans. Telehealth reduces geographic barriers, improves access in underserved areas, and supports chronic disease management.
Smart City Applications: Traffic, Energy, and Public Services
AI extends beyond healthcare into urban management, enhancing efficiency, sustainability, and quality of life. Smart traffic systems in cities such as Hangzhou, Guangzhou, and Xiong’an leverage AI to monitor congestion, predict peak periods, and adjust traffic signal timing dynamically. Real-time optimization decreases commute times, lowers emissions, and enhances emergency vehicle response. These systems incorporate data from IoT sensors, GPS, and mobile applications to provide authorities with actionable insights.
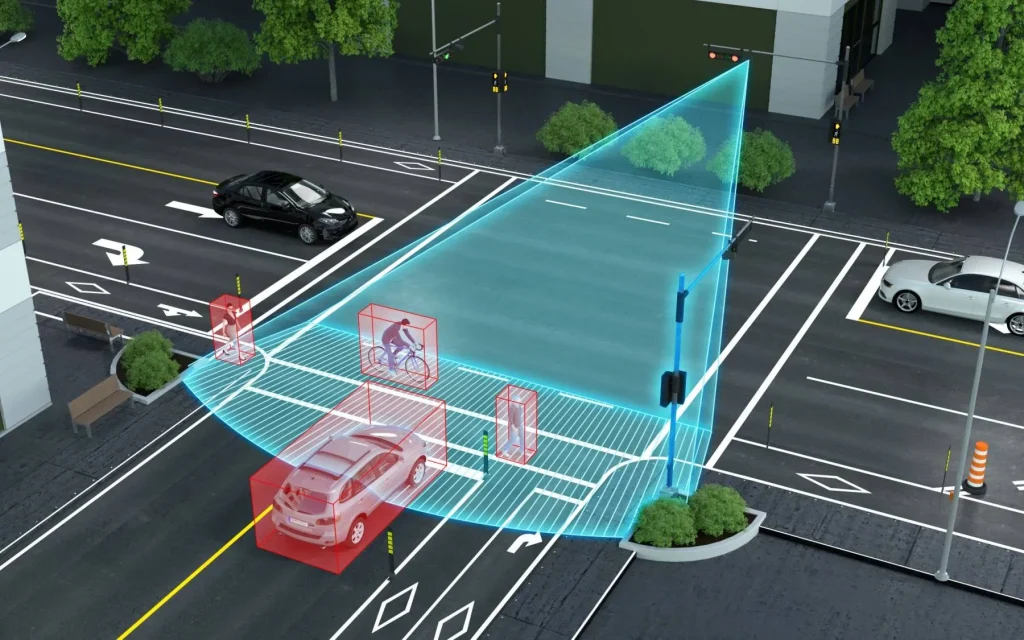
In energy management, AI-driven analytics monitor consumption patterns in public buildings and infrastructure, optimizing electricity distribution and integrating renewable sources. Predictive modeling allows grid operators to balance supply and demand, reduce peak load stress, and maintain efficiency. Environmental monitoring uses AI to analyze air quality, noise levels, and waste management, enabling timely interventions and improving urban sustainability.
Public service management is similarly enhanced. AI platforms coordinate emergency response, monitor public safety through video analytics, and facilitate citizen reporting through mobile apps. Real-time dashboards integrate multiple data sources, allowing municipalities to deploy resources efficiently, respond to crises effectively, and make informed planning decisions.
Challenges in AI Adoption
Despite substantial progress, AI implementation faces several challenges. Data privacy and cybersecurity concerns require robust encryption, access control, and compliance with regulations such as China’s Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL). Interoperability with legacy systems, standardization of AI models, and workforce training remain critical. Hospitals and municipal authorities must ensure human oversight in AI-assisted decision-making, maintaining ethical and clinical accountability.
Technical limitations, including algorithm interpretability and integration complexity, can hinder large-scale adoption. Organizations must invest in talent development, infrastructure, and monitoring protocols to maximize AI’s benefits while minimizing operational and ethical risks.
Future Prospects
The integration of AI with robotics, edge computing, and 5G networks is expected to further revolutionize healthcare and urban management. Autonomous emergency response systems, AI-assisted surgical procedures, and predictive urban planning are on the horizon. Cross-sector collaboration between government agencies, private technology firms, and academic institutions will accelerate innovation while ensuring compliance, ethical oversight, and scalable deployment. AI applications in healthcare and urban management are projected to improve operational efficiency by 20–30% over the next five years and enhance patient and citizen experiences significantly.
Conclusion: Pioneering AI for Societal and Urban Advancement
China’s AI adoption in healthcare and smart cities represents a strategic blend of innovation, governance, and practical utility. In hospitals, AI improves diagnostic accuracy, predictive planning, and operational efficiency, while telemedicine extends access to underserved populations. In urban infrastructure, AI enhances traffic management, energy efficiency, public safety, and environmental sustainability. Addressing data privacy, system interoperability, and workforce readiness will be crucial for continued success. As AI technologies mature, China is poised to redefine healthcare delivery and urban management, setting a global example for integrated, intelligent, and data-driven innovation.






