China’s AI Governance and Policy Framework: Balancing Innovation and Ethics

China’s rapid advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) have positioned the country as a global leader in emerging technologies. With AI influencing sectors ranging from healthcare and finance to smart cities and autonomous systems, the need for robust governance and policy frameworks has become critical. The Chinese government, alongside regulatory authorities and industry bodies, has established comprehensive strategies to ensure that AI development is ethical, secure, and aligned with national objectives. This blog explores the current state of AI governance in China, policy initiatives, ethical considerations, industry impacts, and future prospects, providing insight into how China balances technological innovation with societal responsibility.
Strategic Importance of AI Governance
AI is considered a strategic asset for China, driving economic growth, national security, and technological competitiveness. The government has integrated AI governance into national development plans such as the “New Generation Artificial Intelligence Development Plan,” emphasizing ethical deployment, standardization, and alignment with industrial and social priorities. Governance frameworks aim to mitigate risks associated with autonomous decision-making, data misuse, and unintended consequences, ensuring that AI applications contribute positively to economic and societal outcomes. Regulatory oversight is designed to create an environment where innovation can flourish without compromising public trust or safety.
Policy Initiatives and Regulatory Frameworks
China’s AI policy landscape involves multiple government bodies, including the Ministry of Science and Technology, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, and the Cyberspace Administration of China. Policies address key areas such as data protection, algorithmic transparency, security compliance, and accountability mechanisms. Guidelines encourage developers to create explainable AI models, maintain robust data privacy, and adhere to standardized operational protocols. Pilot programs in sectors like healthcare, finance, and smart cities are monitored to assess regulatory compliance, inform national standards, and guide broader implementation.
Policy instruments also focus on fostering research and development while minimizing risks. Incentives, funding programs, and industrial standards support domestic innovation in AI algorithms, hardware, and applications. Ethical frameworks outline principles for fairness, accountability, and human-centric AI design. By formalizing governance, China ensures that AI deployment aligns with strategic objectives while safeguarding societal interests.
Ethical Considerations in AI Deployment
Ethics is central to China’s AI governance approach. Key concerns include algorithmic bias, decision transparency, privacy protection, and social impact. Developers are required to implement explainable AI techniques, enabling auditors and users to understand decision-making processes. In sensitive areas such as healthcare diagnostics, autonomous vehicles, and financial credit assessment, ethical standards ensure that AI does not produce harmful or discriminatory outcomes. Ethical oversight promotes trust among citizens, regulators, and industry stakeholders, supporting broader adoption of AI technologies across diverse sectors.
AI Governance in Practice: Industry Applications
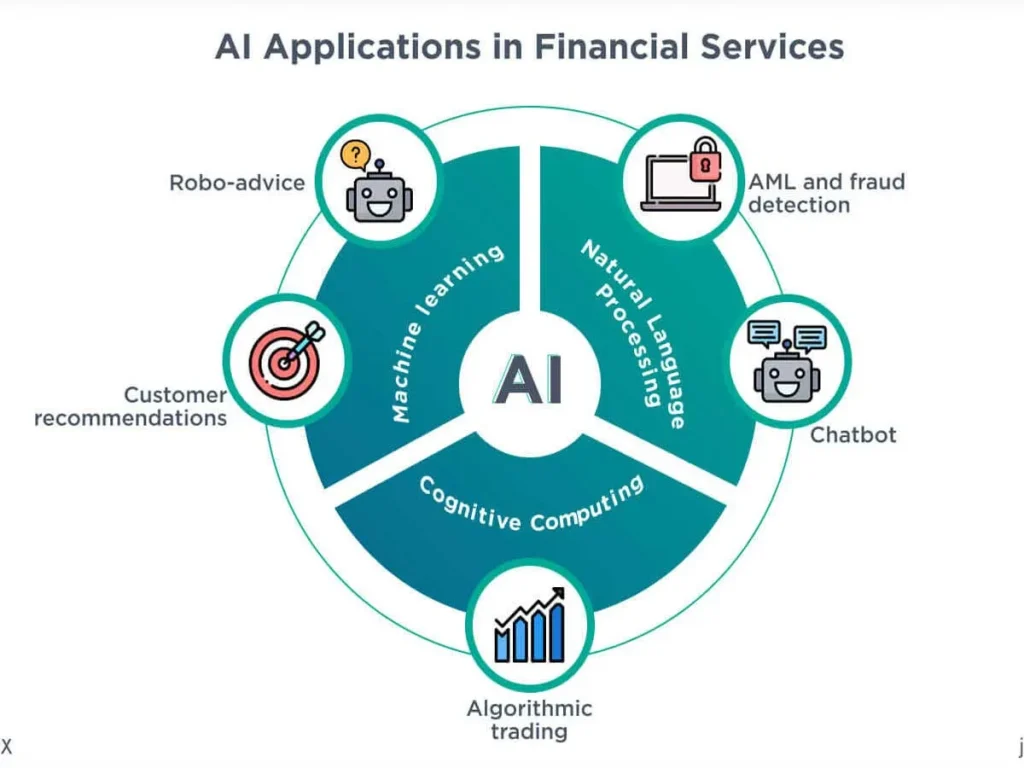
Governance policies are applied across various industries to ensure responsible AI adoption. In healthcare, hospitals implement AI systems for diagnostics and predictive analytics while adhering to data privacy regulations. Financial institutions employ AI for credit scoring, fraud detection, and algorithmic trading under regulatory scrutiny. In smart cities, AI traffic management and energy optimization systems follow national standards for safety, transparency, and accountability. These applications demonstrate how governance frameworks translate into operational practices that balance efficiency with ethical responsibility.
Challenges and Implementation Barriers
Despite structured policies, China faces challenges in AI governance. Rapid technological evolution can outpace regulatory adaptation, creating gaps in oversight. Integrating AI into complex organizational processes requires technical expertise, infrastructure investment, and workforce training. Ensuring interoperability between AI systems, maintaining cybersecurity, and addressing societal concerns around algorithmic decisions are ongoing challenges. Policymakers and industry leaders collaborate to develop adaptive governance strategies, pilot testing frameworks, and dynamic standards to mitigate risks effectively.
International Collaboration and Global Implications
China actively engages in international AI governance dialogue, contributing to standardization efforts and ethical frameworks at global forums. Collaboration with foreign research institutions and multinational corporations facilitates knowledge exchange, benchmarking, and alignment with international best practices. By participating in global discussions, China positions itself as a leader in responsible AI development, influencing international policies while advancing domestic innovation.
Future Directions and Strategic Outlook
The future of AI governance in China involves integrating emerging technologies such as quantum computing, autonomous systems, and edge AI into regulatory frameworks. Continuous refinement of policies, ethical standards, and compliance mechanisms will support scalable, safe, and transparent deployment. Strengthening public trust through accountability, transparency, and human-centric design remains a priority. AI governance will increasingly emphasize sustainability, equitable access, and alignment with long-term national development goals.
Conclusion: Ensuring Responsible AI Innovation
China’s AI governance framework exemplifies a strategic balance between fostering innovation and ensuring ethical, secure, and socially responsible deployment. Comprehensive policy initiatives, ethical guidelines, industry compliance mechanisms, and international collaboration collectively create a robust ecosystem for AI development. By addressing technical, ethical, and operational challenges, China ensures that AI technologies contribute to economic growth, public welfare, and global competitiveness. The governance model demonstrates how structured oversight and strategic planning can enable innovation while safeguarding societal interests, positioning China as a global leader in responsible AI.