AI Applications in Healthcare And Smart Cities: Transforming China’s Urban Landscape
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly reshaping China’s healthcare systems and urban infrastructure, enabling more efficient medical services, intelligent city management, and data-driven decision-making. The integration of AI technologies in hospitals, public health monitoring, and smart city operations demonstrates the country’s commitment to leveraging innovation for social benefit, economic efficiency, and sustainable development. From predictive analytics and diagnostics to traffic management and energy optimization, AI applications are redefining how Chinese cities operate and how citizens access essential services. This blog explores the current deployment of AI in healthcare and smart cities, highlights technological trends, analyzes data-driven outcomes, and evaluates future prospects.
AI in Healthcare: Enhancing Diagnostics and Patient Care
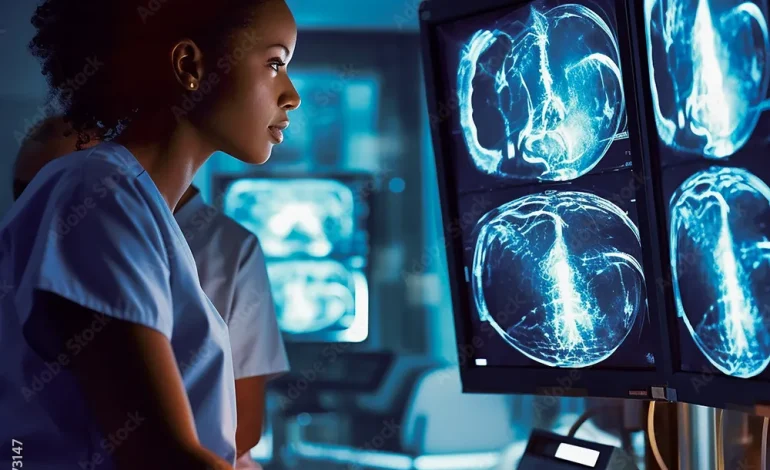
AI adoption in Chinese hospitals is primarily focused on diagnostics, predictive analytics, and operational efficiency. Advanced machine learning algorithms analyze medical imaging, such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs, improving accuracy and enabling early detection of conditions like cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurological disorders. Hospitals in Beijing, Shanghai, and Shenzhen have implemented AI-assisted imaging platforms, which reduce diagnostic errors by up to 20% and accelerate the review process, allowing radiologists to focus on complex cases.
Predictive analytics is another critical application. AI models process electronic health records, demographic data, and patient history to identify high-risk individuals, forecast disease progression, and optimize treatment plans. For example, predictive algorithms are used to monitor ICU patients in major hospitals, alerting medical staff to potential complications before they become critical. This proactive approach reduces mortality rates, enhances operational efficiency, and improves patient outcomes while lowering hospital costs.
AI also supports hospital operations beyond clinical diagnostics. Intelligent scheduling systems optimize staff deployment, operating room utilization, and patient appointment management. Administrative tasks, such as billing, record-keeping, and claims processing, are increasingly automated through AI-driven platforms. By reducing human error and streamlining operations, hospitals achieve higher efficiency, faster service delivery, and improved patient satisfaction.
Telemedicine and Remote Healthcare
Telemedicine is expanding rapidly, particularly in rural and underserved areas of China. AI-powered telehealth platforms enable remote consultations, virtual diagnostics, and monitoring for patients who cannot access urban hospitals. Algorithms analyze patient-reported symptoms and medical history to assist healthcare professionals in triaging cases and providing evidence-based recommendations. Mobile applications integrate AI with wearable devices, offering real-time monitoring of vitals, blood glucose, and heart rate. This integration enhances accessibility, continuity of care, and early intervention, bridging the gap between urban medical resources and rural populations.
AI in Smart Cities: Urban Efficiency and Sustainability
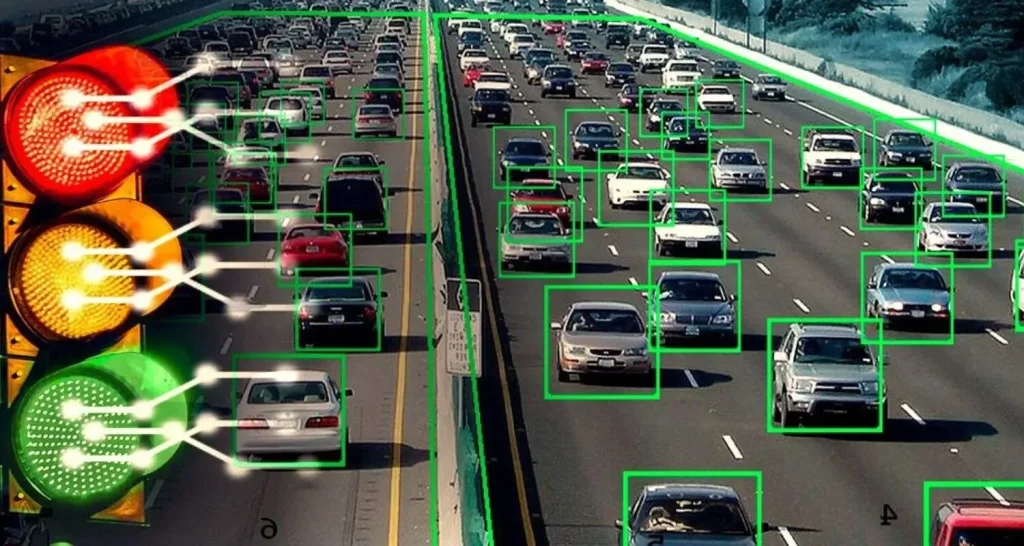
AI applications in smart cities focus on traffic management, energy optimization, public safety, and resource allocation. Cities like Hangzhou, Xiong’an, and Guangzhou have implemented AI-driven traffic systems that monitor congestion, optimize signal timing, and predict high-traffic periods. Real-time traffic analysis reduces commute times by up to 15%, lowers vehicle emissions, and enhances emergency response coordination.
In energy management, AI algorithms analyze consumption patterns from smart grids, sensors, and meters to optimize electricity distribution, integrate renewable sources, and reduce peak loads. AI-assisted environmental monitoring tracks air and water quality, noise levels, and waste management efficiency. Data-driven insights enable municipal authorities to implement targeted interventions, improving sustainability and urban livability.
Public safety also benefits from AI applications. Video analytics, facial recognition, and predictive policing models help monitor urban areas, identify security risks, and deploy law enforcement resources efficiently. Smart city platforms integrate multiple data sources, allowing governments to respond rapidly to emergencies, coordinate resources, and improve citizen services.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite significant progress, challenges persist in integrating AI into healthcare and smart cities. Data privacy, cybersecurity, interoperability with legacy systems, and ethical concerns about algorithmic decision-making remain critical issues. Hospitals and city authorities must ensure robust regulatory compliance, secure storage of sensitive information, and transparency in AI-driven decisions. Talent shortages in AI engineering, data science, and system maintenance also pose constraints, requiring ongoing training and workforce development programs.
Future Prospects
The future of AI in China’s healthcare and urban management is promising. Integration of AI with robotics, edge computing, and 5G networks will enhance automation, real-time analytics, and predictive capabilities. Emerging applications include autonomous emergency response vehicles, AI-assisted surgical systems, and fully optimized energy grids. Cross-sector collaboration between government, industry, and academia will accelerate innovation while ensuring ethical and responsible deployment.
Conclusion: Redefining Urban Life and Healthcare Delivery
AI technologies are transforming both healthcare and urban systems in China, offering efficiency, improved service quality, and data-driven decision-making. Hospitals leverage AI for diagnostics, predictive analytics, and operational optimization, while smart cities utilize real-time data and intelligent systems to enhance traffic flow, energy use, and public safety. By addressing technical, ethical, and workforce challenges, China is building a resilient ecosystem for AI-driven solutions. These innovations not only improve daily life but also position the country as a global leader in applied artificial intelligence, shaping the future of sustainable, intelligent urban environments and advanced healthcare delivery.