Robotics and AI in China’s Manufacturing Hubs
China’s manufacturing sector is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by the integration of robotics and artificial intelligence (AI). Once reliant on labor-intensive production, factories across Shenzhen, Suzhou, and Shanghai are increasingly adopting automation technologies to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and maintain competitiveness on a global scale. This shift aligns with national strategic initiatives aimed at modernizing industrial infrastructure and promoting smart manufacturing as a cornerstone of the “Made in China 2025” vision. The convergence of robotics, AI, and digital control systems is not only reshaping production workflows but also redefining workforce requirements, supply chain coordination, and quality assurance protocols.
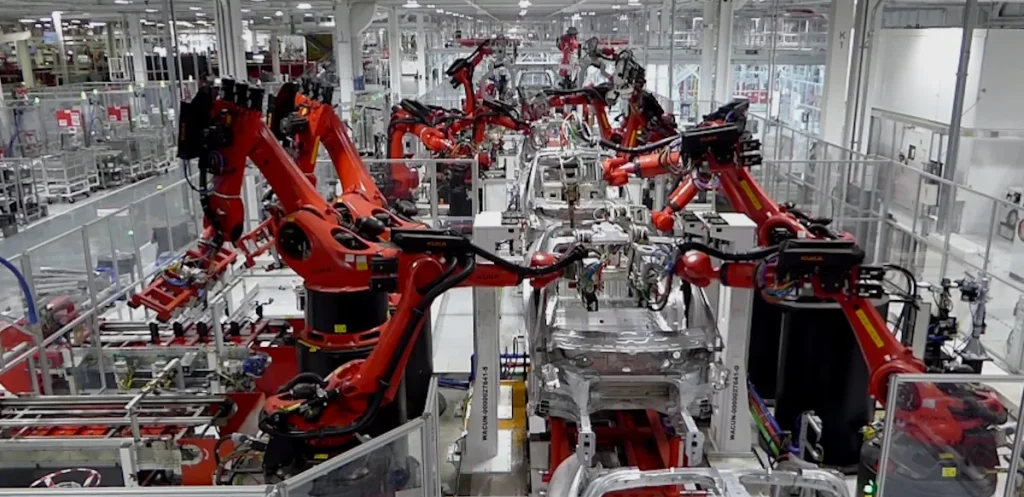

Automation as a Strategic Imperative
The adoption of industrial robotics in Chinese factories addresses several pressing economic and operational challenges. Rising labor costs and demographic shifts have made traditional manufacturing models less sustainable, prompting enterprises to invest in automation technologies. Robotics systems, equipped with advanced sensors and AI algorithms, now perform tasks ranging from precision assembly and welding to packaging and quality inspection. By integrating AI-driven decision-making, these systems can self-adjust to optimize production efficiency, predict maintenance needs, and reduce downtime. Leading manufacturing hubs such as the Pearl River Delta have reported productivity gains of up to 30% in facilities implementing high-end robotics, illustrating the tangible benefits of this technological shift.
AI-Enhanced Quality and Predictive Maintenance
AI is playing a crucial role in enhancing manufacturing quality and operational reliability. Machine learning algorithms analyze production data in real time to detect anomalies, predict equipment failures, and recommend adjustments in process parameters. For instance, semiconductor and electronics manufacturing lines employ AI-driven vision systems to identify microscopic defects that would be difficult for human inspectors to detect consistently. Predictive maintenance powered by AI ensures that machinery operates efficiently, reducing both operational costs and the likelihood of unplanned production halts. These innovations contribute to higher product quality, shorter lead times, and increased competitiveness in both domestic and international markets.
Supply Chain Integration and Smart Factories
The robotics and AI revolution extends beyond individual production lines to encompass integrated supply chain management. Smart factories in China are increasingly connected to upstream suppliers and downstream logistics partners via IoT-enabled platforms, allowing real-time monitoring of inventory, shipment, and production status. This connectivity facilitates more agile responses to demand fluctuations and supply chain disruptions, which has been particularly important in the context of recent global trade uncertainties. By combining robotics, AI, and digital supply chain solutions, manufacturers are creating resilient ecosystems capable of scaling operations while maintaining precision and quality standards.
Workforce Implications and Talent Development
The shift toward AI-driven robotics has significant implications for workforce planning. While automation reduces reliance on manual labor for repetitive tasks, it simultaneously increases demand for highly skilled personnel capable of programming, monitoring, and maintaining advanced machinery. Chinese universities, technical institutes, and corporate training programs have expanded offerings in robotics engineering, AI applications, and industrial automation. Collaborative initiatives between academia and industry focus on practical skills, research projects, and internships, ensuring a pipeline of talent equipped to support ongoing innovation in manufacturing hubs.
Global Competitiveness and Industry Impact
China’s emphasis on robotics and AI in manufacturing is contributing to a shift in global industrial competitiveness. By embracing advanced technologies, domestic firms can offer higher-quality products at competitive costs, while simultaneously reducing dependency on foreign suppliers of automation and AI solutions. This has implications for global trade dynamics, particularly in electronics, automotive, and high-precision manufacturing sectors. Moreover, the success of China’s smart factories serves as a model for other emerging economies seeking to modernize industrial operations, further amplifying the country’s influence in the global manufacturing ecosystem.
Challenges and Technological Hurdles
Despite significant progress, challenges remain in scaling AI and robotics adoption. High initial investment costs, integration complexities, and technology standardization issues can hinder implementation, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises. Additionally, ensuring cybersecurity across connected smart factories is critical, as vulnerabilities in IoT and AI systems could disrupt operations or compromise sensitive production data. Continuous innovation, government support, and collaboration with international partners will be essential to overcome these obstacles and sustain momentum in the robotics-driven industrial transformation.
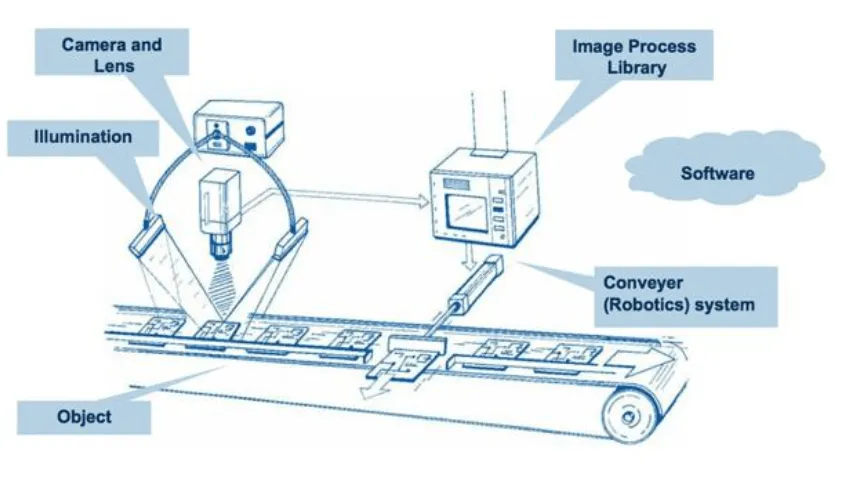
Conclusion: Pioneering the Future of Manufacturing
China’s manufacturing hubs exemplify how robotics and AI can drive industrial modernization and global competitiveness. By integrating automation technologies, predictive analytics, and smart supply chain solutions, Chinese factories are achieving higher productivity, improved quality, and operational resilience. Talent development programs, coupled with government initiatives, are equipping the workforce with the skills necessary to sustain this technological evolution. As these advancements continue, China is poised to set new benchmarks in industrial efficiency and innovation, offering valuable insights for manufacturing strategies worldwide.





