Robotics startups are powering factories, logistics hubs, and even healthcare.
From Hardware Hub to Robotics Powerhouse
For years, Shenzhen was known as the world’s hardware capital, producing smartphones, drones, and consumer electronics at breakneck speed. Today, the city is undergoing another transformation: it has become China’s industrial robotics hub, where startups, research labs, and manufacturers converge to drive automation.
This shift reflects both domestic demand rising wages and labor shortages and Beijing’s push for “Made in China 2025”, which prioritizes smart manufacturing as the backbone of economic resilience.
Startups at the Forefront
Shenzhen’s robotics startups span a wide spectrum:
- Factory automation: Companies building robotic arms for electronics assembly.
- Logistics: AI-driven warehouse robots reducing delivery times for e-commerce giants.
- Healthcare: Surgical robots and service bots piloted in hospitals.
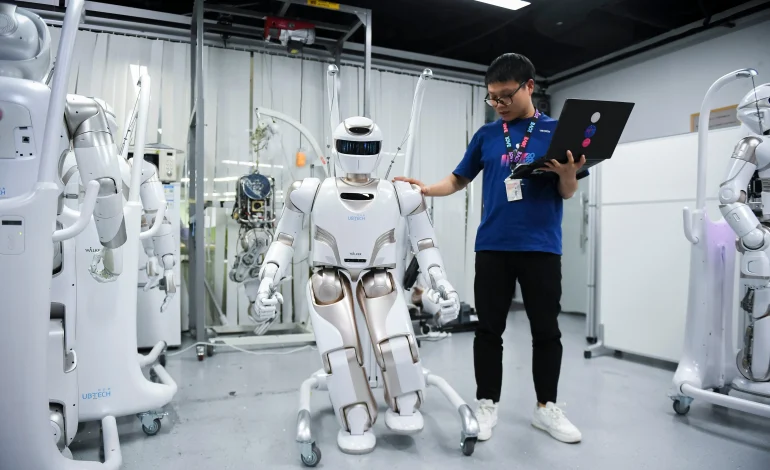
One standout is UBTech Robotics, best known globally for humanoid robots but now also supplying automation solutions for logistics and education. Another, Geek+, has built a global reputation in warehouse robotics, competing with Amazon’s Kiva Systems.
AI and Sensors Integration
The key advantage of Shenzhen’s ecosystem is integration. Robotics here isn’t just mechanical; it’s powered by AI, machine vision, and advanced sensors.
Startups are embedding robotics into industrial IoT platforms, enabling predictive maintenance, real-time quality checks, and energy optimization. The result: factories that are not just automated but data-driven and adaptive.
Global Supply Chain Role
China’s export economy is increasingly dependent on robotics to maintain competitiveness. As Western buyers push for lower costs and faster delivery, Shenzhen’s robotic automation reduces dependence on manual labor.
This has spillover effects: robotics startups are exporting not just hardware but also end-to-end smart factory solutions to Southeast Asia, Latin America, and Africa effectively exporting automation as a service.
Financing the Robot Boom
Industrial robotics is capital-intensive. Startups require huge investments for R&D, prototyping, and scaling. Shenzhen has attracted both venture capital and state-backed funds, making it one of the most heavily funded robotics hubs outside the U.S.
Some firms are also experimenting with digital financing models to streamline procurement and supplier payments. Pilot programs have explored blockchain-based settlement systems to help SMEs adopt robotics with lower upfront costs, ensuring smoother cash flow. Such financial innovations quietly underpin the city’s automation drive.
The Labor Question
While robotics promises efficiency, it also raises social questions. Factory workers face displacement, and local governments must balance automation with employment stability.
To mitigate risks, Shenzhen is promoting reskilling programs, helping workers transition into robot maintenance, programming, and systems integration roles. The narrative is shifting from “robots replacing humans” to “humans working with robots.”
Global Competition
Shenzhen is not alone. Germany’s KUKA, Japan’s Fanuc, and U.S.-based Boston Dynamics remain global leaders. Yet Chinese firms are closing the gap quickly, offering cost-effective alternatives at scale.
The geopolitical dimension looms as well: U.S. restrictions on high-end chips and AI components could slow China’s robotics sector. But domestic efforts to build homegrown chips and AI accelerators aim to reduce this dependency.
Outlook: Shenzhen as the Testbed
Shenzhen’s rise as automation capital underscores how China leverages its unique ecosystem of manufacturing, capital, and policy support to stay ahead.
By 2030, the city may not only supply robotics to the world but also pioneer new models of autonomous factories, logistics hubs, and even hospitals, where robots become routine infrastructure.
For global readers, Shenzhen offers a preview of how the next industrial revolution will unfold in labs, warehouses, and assembly lines where robots quietly reshape the backbone of the global economy.